Tongariro: Difference between revisions
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
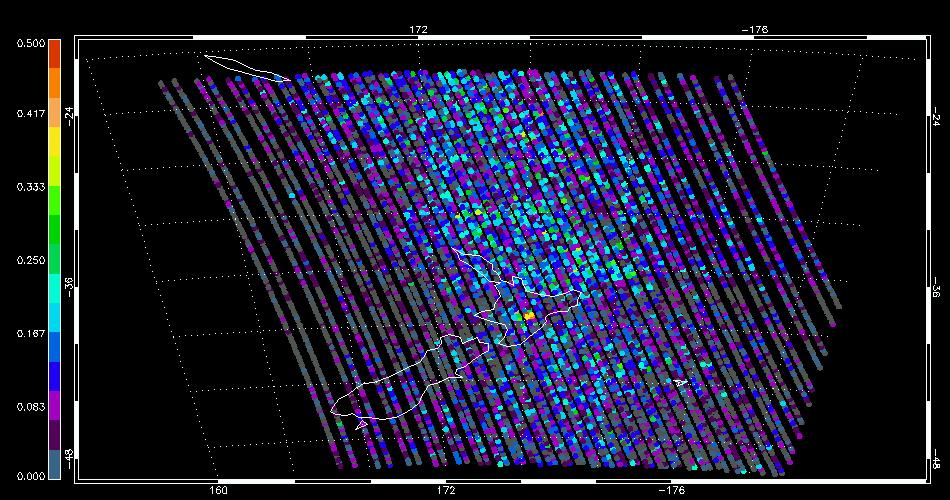
The SO<sub>2</sub> anomaly flag <ref>Carboni, E., R.G. Grainger, J.C. Walker, A. Dudhia and R. Siddans, A new scheme for sulphur dioxide retrieval from IASI measurements: application to the Eyjafjallajökull eruption of April and May 2010, Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12, 11417—11434, 2012.</ref> for [[IASI]] overpass at X.X on the X November shows four anomalous pixels surrounding the location of Mt Tongariro. The SO<sub>2</sub> had passed below the dectable limit by the time of the next overpass at Y.Y. | The SO<sub>2</sub> anomaly flag <ref>Carboni, E., R.G. Grainger, J.C. Walker, A. Dudhia and R. Siddans, A new scheme for sulphur dioxide retrieval from IASI measurements: application to the Eyjafjallajökull eruption of April and May 2010, Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12, 11417—11434, 2012.</ref> for [[IASI]] overpass at X.X on the X November shows four anomalous pixels surrounding the location of Mt Tongariro. The SO<sub>2</sub> had passed below the dectable limit by the time of the next overpass at Y.Y. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 07:47, 14 December 2012
| Tongariro | |
|---|---|
| Elevation | 1978 m |
| Latitude | 39° 08′ 00″ S |
| Longitude | 175° 38′ 30″ E |
Tongariro is a compound volcano in the Taupo Volcanic Zone of the North Island of New Zealand.
Eruptions
6 August 2012 23:52 NZST (6 August 2012 10:52 GMT)
After a couple of weeks of increased earthquake activity and changes in gas emission, Mount Tongariro had a phreatic (gas and steam driven) eruption on Monday 6 August 2012 at 11.52 pm NZST. The eruption lasted only a couple of minutes and occurred partly from existing vents at the Upper Te Maari Crater.[1]
21 November 2012 13:24:50 NZDT (21 November 2012 00:24:50 GMT)
At 1:24 pm NZDT on the 21 November 2012 an eruption of the Upper Te Maari crater ejected ash to a height of 3-4 km. the eruption lasted approx 5 min.[2] A nearby walking party took a video of the eruption showing the rapid ascent of the ash plume.[3] The eruption was measured by GNS who produced a Tongariro eruption time series.
The SO2 anomaly flag [4] for IASI overpass at X.X on the X November shows four anomalous pixels surrounding the location of Mt Tongariro. The SO2 had passed below the dectable limit by the time of the next overpass at Y.Y.
References
- ↑ http://www.gns.cri.nz/Home/Learning/Science-Topics/Volcanoes/New-Zealand-Volcanoes/Tongariro/Eruption-6-August-2012
- ↑ http://www.gns.cri.nz/Home/Learning/Science-Topics/Volcanoes/New-Zealand-Volcanoes/Tongariro/Tongariro-latest
- ↑ http://www.nzherald.co.nz/nz/news/article.cfm?c_id=1&objectid=10849136
- ↑ Carboni, E., R.G. Grainger, J.C. Walker, A. Dudhia and R. Siddans, A new scheme for sulphur dioxide retrieval from IASI measurements: application to the Eyjafjallajökull eruption of April and May 2010, Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12, 11417—11434, 2012.